Struggling with high visceral fat? Try these 10 powerful foods to reduce it!

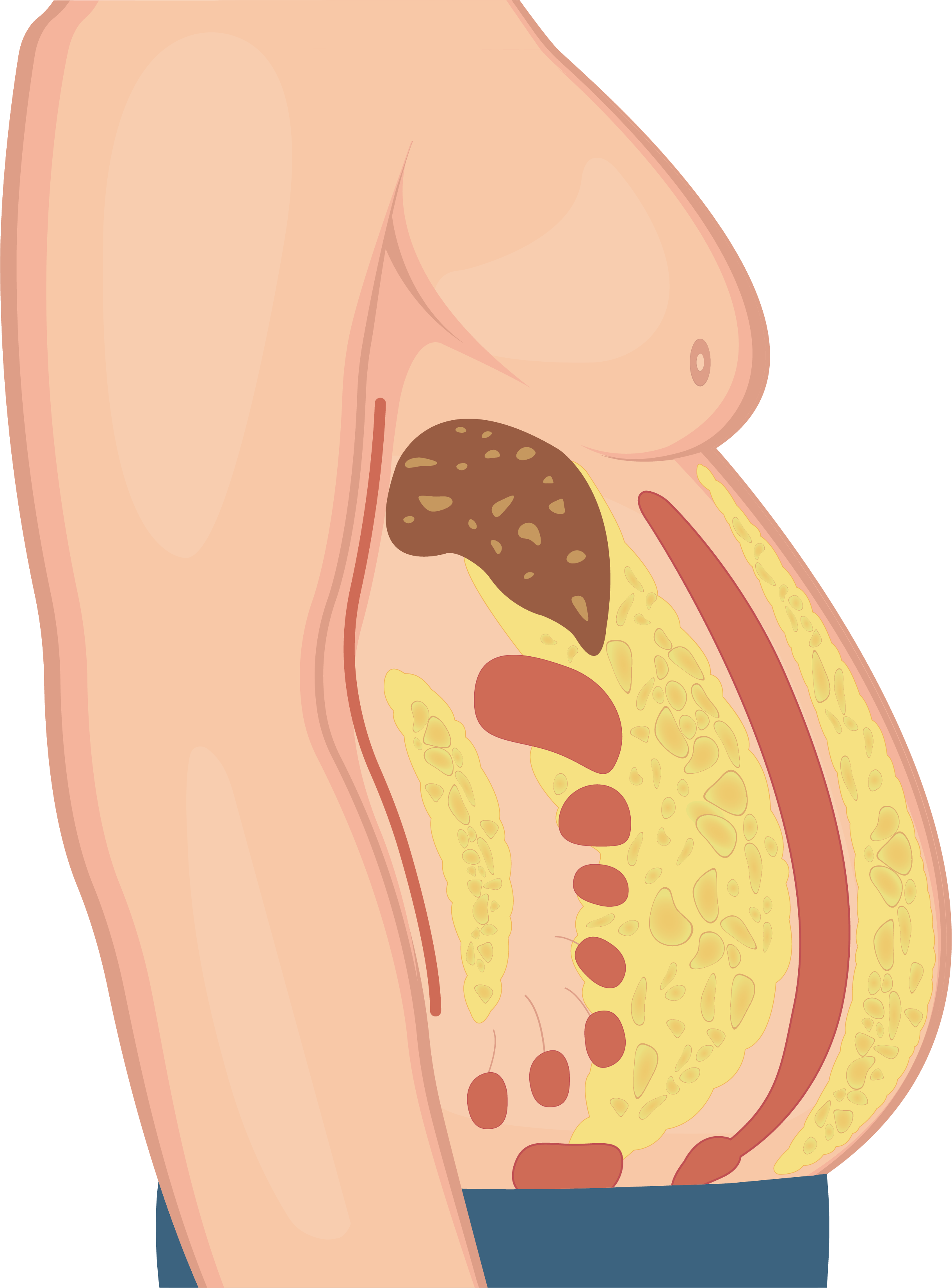
What is Visceral Fat?
Body fat can be divided into visceral fat and subcutaneous fat. But what is the difference between the two?
• Subcutaneous Fat (Pear-shaped obesity)
Primarily functioning to maintain body temperature and cushion external impacts, it is concentrated in the hips, thighs, and limbs, and more commonly observed in women.
• Visceral Fat (Apple-shaped obesity)
Mainly for storing energy and protecting internal organs, it is generally found surrounding the abdominal cavity, intestines, stomach, liver, heart, kidneys, and other organs. Because it is primarily concentrated in the abdomen, it is also known as central obesity, and is commonly seen in men. Visceral fat is more likely to cause various diseases, such as arteriosclerosis, issues related to high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high cholesterol, and cardiovascular diseases, making it more dangerous compared to subcutaneous fat.
How to measure visceral fat?
The most accurate measurements can be obtained through Computed Tomography (CT) or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans. Alternatively, a body fat analyzer can be used, which measures body resistance through a weak electric current and calculates the fat percentage based on multiple personal data inputs. However, the results can vary due to differences in the body’s water content, so it is best to use the same body fat analyzer at the same time of day for more accurate measurements. The simplest method is to measure the waist circumference. If a man’s waist circumference exceeds 90 cm or a woman’s exceeds 80 cm, it is considered that their visceral fat is excessive.
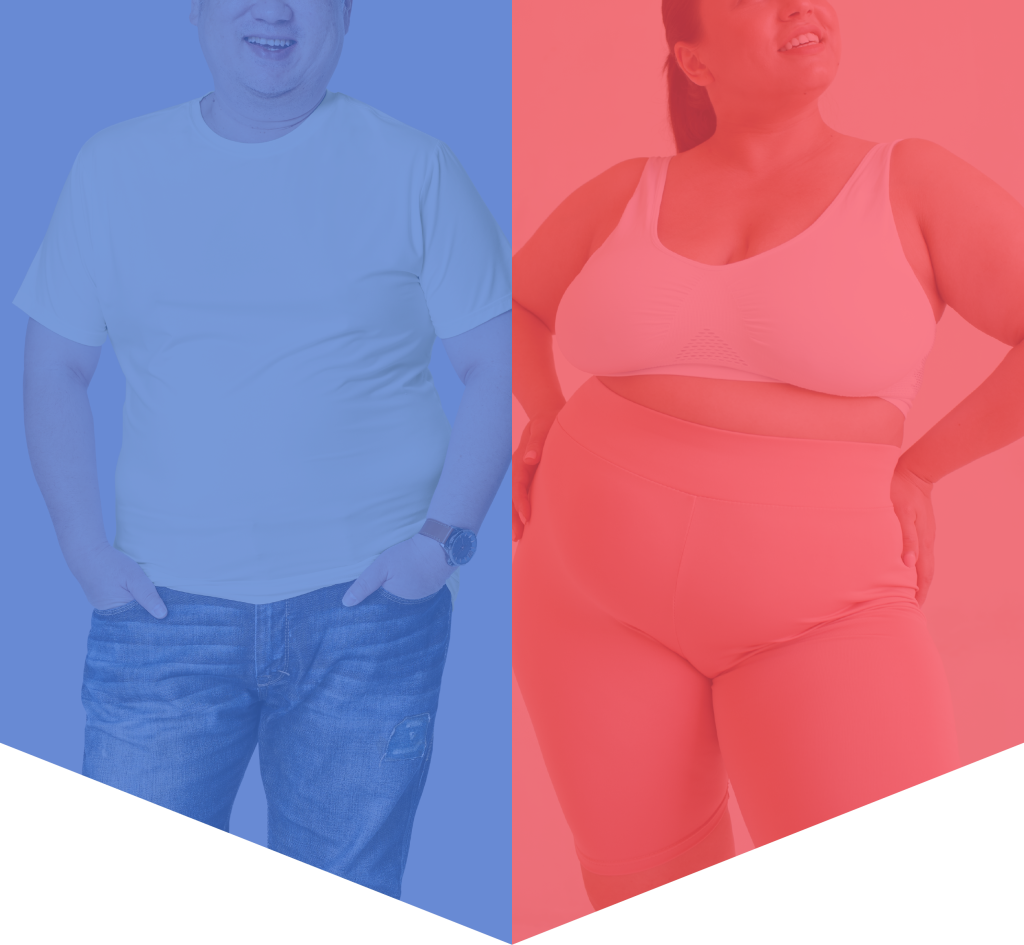

A Simple Method to Measure
Waist Circumference
Male Waistline
> 90 cm
Female Waistline
> 80 cm
Here are 10 foods to help you reduce visceral fat:

Green Vegetables
Spinach, kale, and other leafy greens are rich in dietary fiber, particularly soluble fiber, which promotes bowel movements and reduces fat absorption.

Whole Grains
Whole grain foods such as brown rice and oats help stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce fat accumulation.
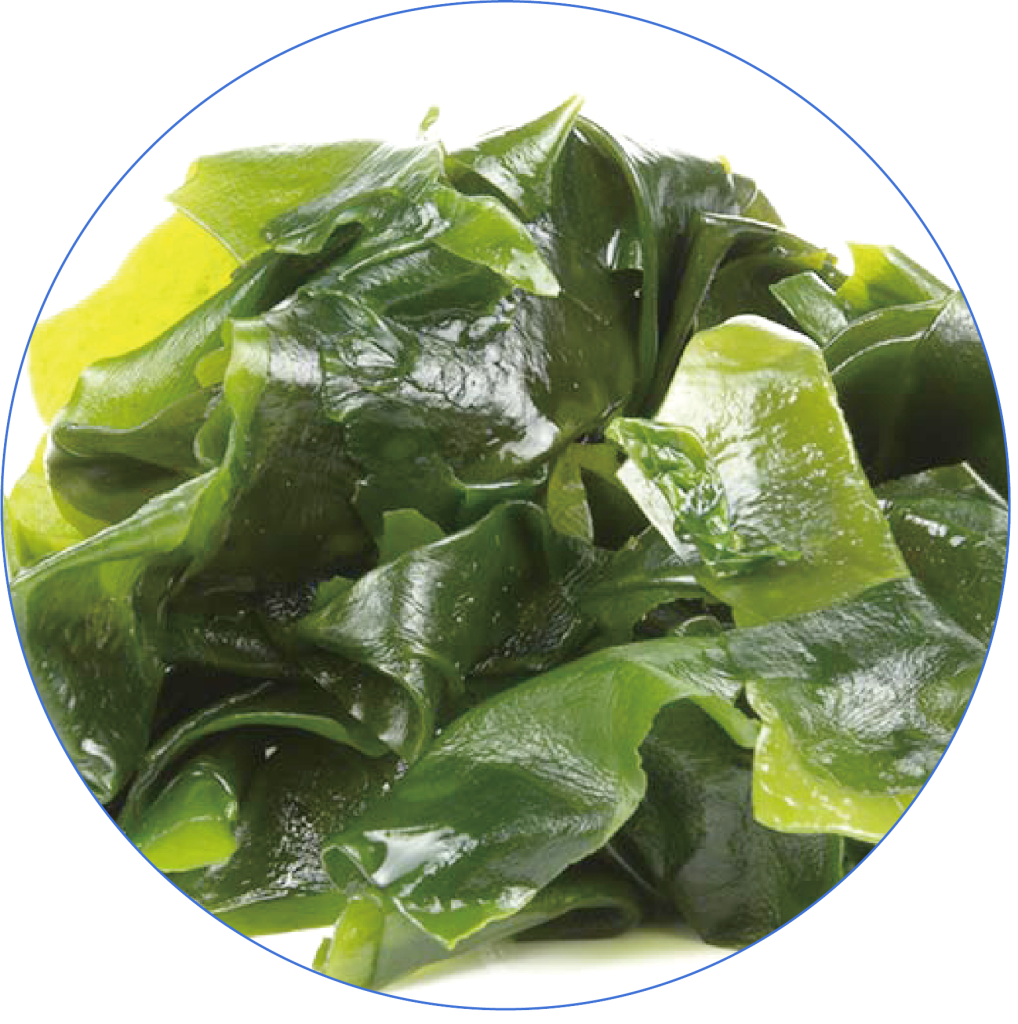

Seaweed
Seaweed (such as wakame) is rich in water-soluble fiber, which aids in weight loss, burning visceral fat, and lowering insulin levels.
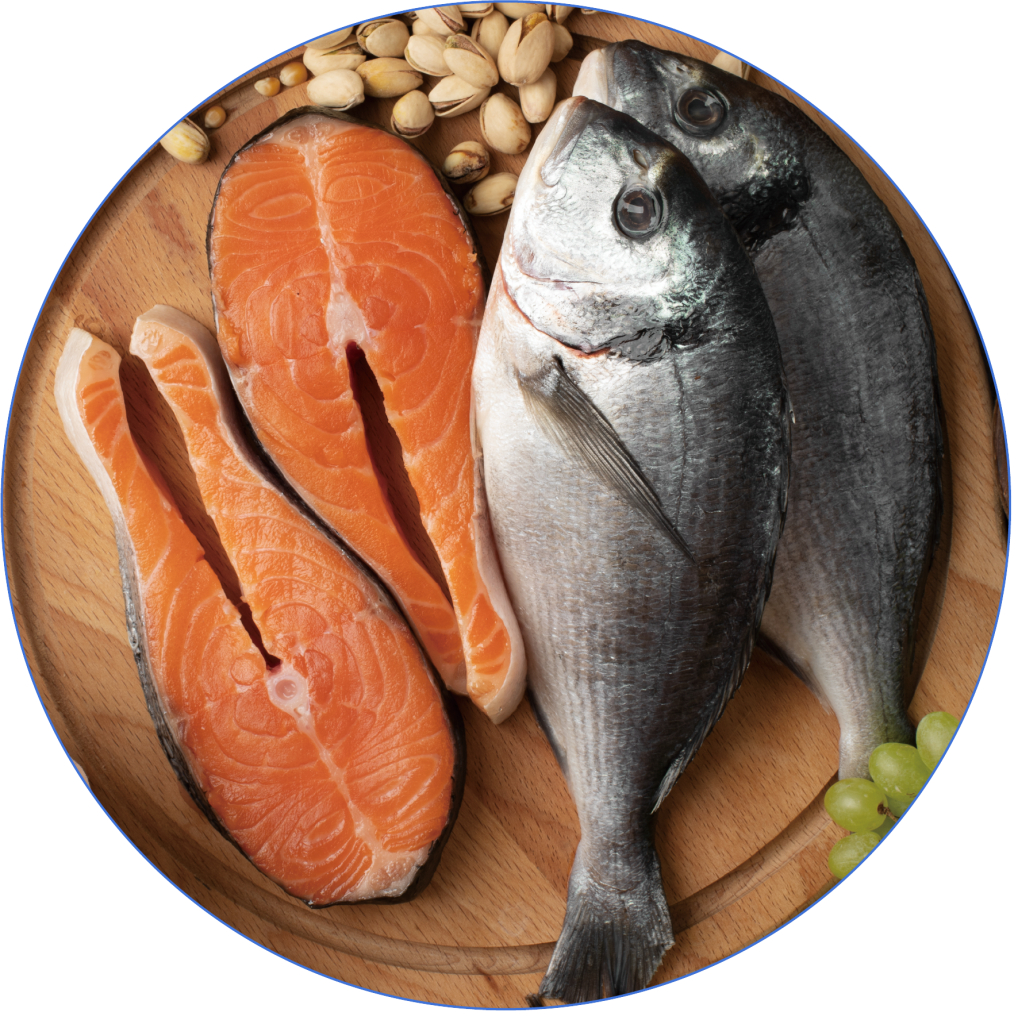

Fish
Fish rich in Omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon and sardines, have anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce visceral fat.
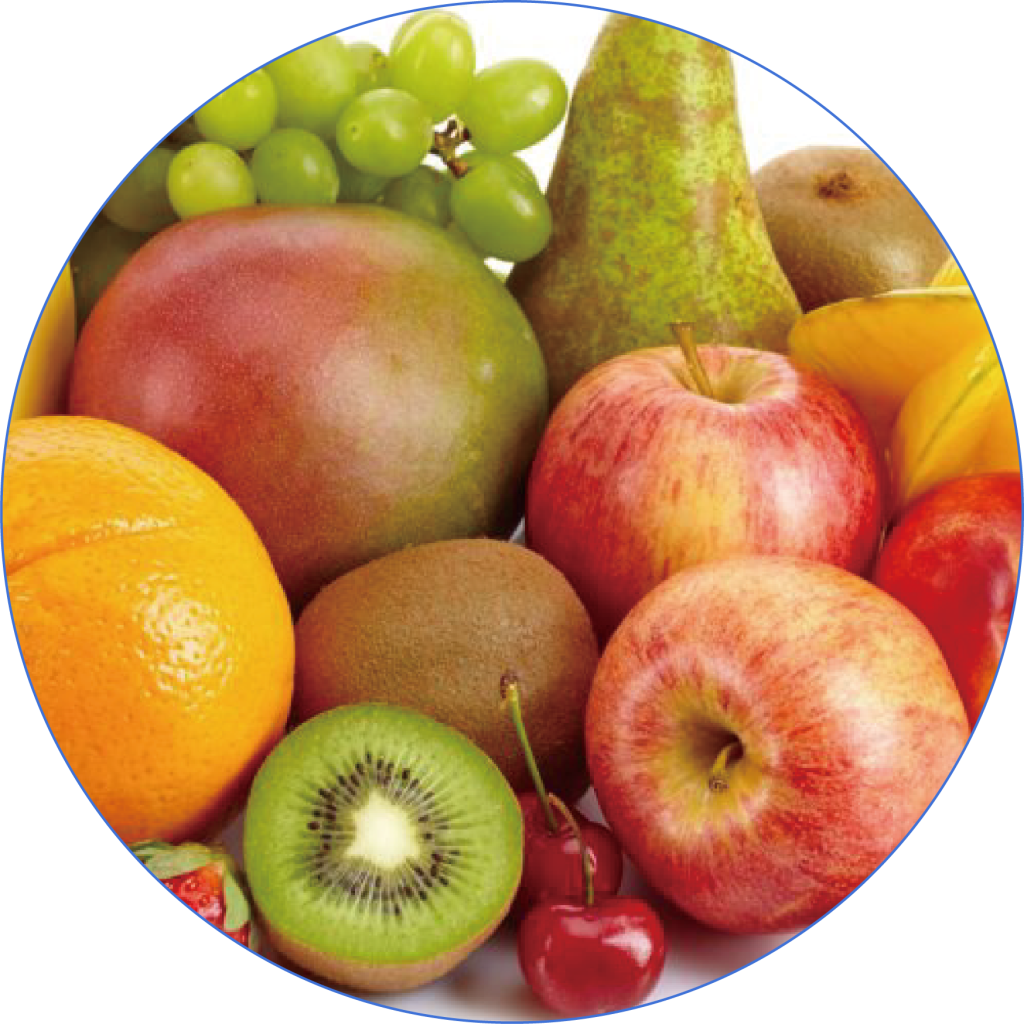

Fruits
Low-sugar fruits like apples and pears are high in dietary fiber and antioxidants, which help reduce fat accumulation.
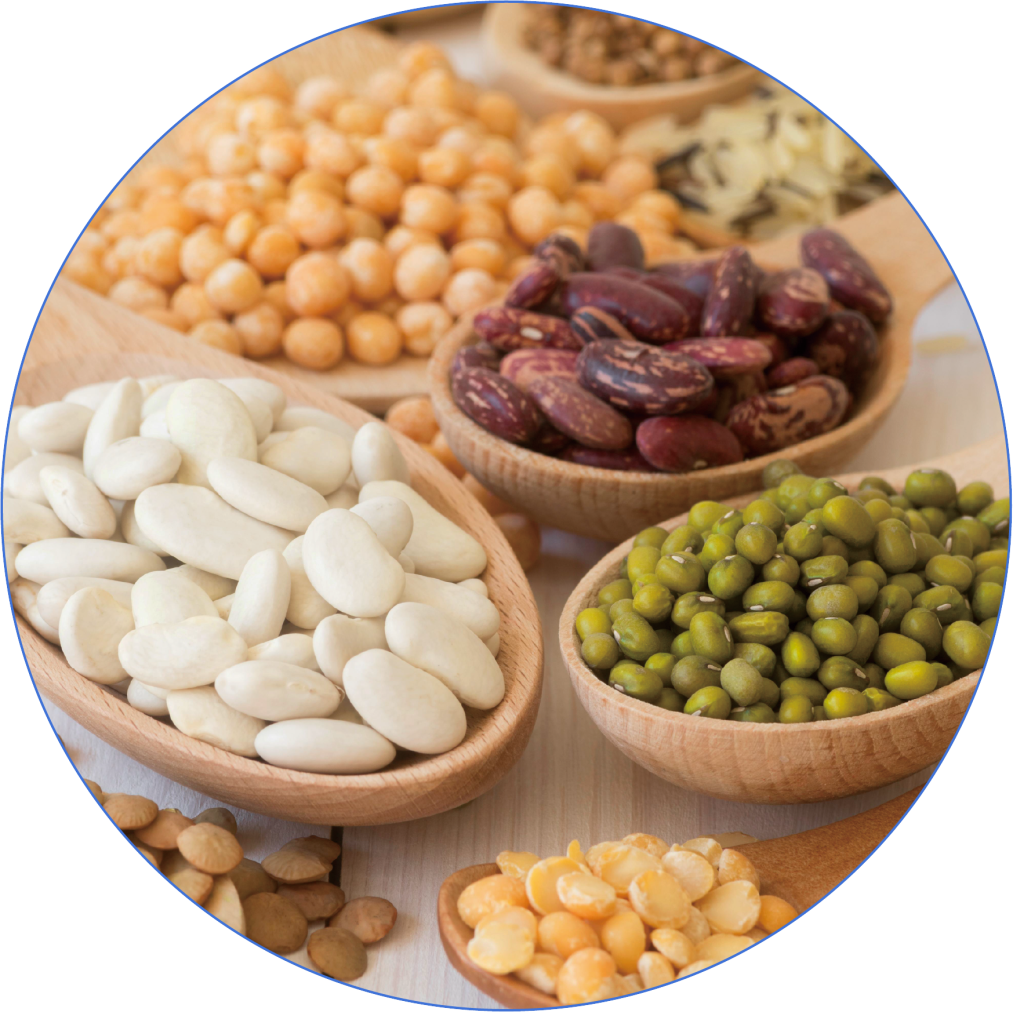

Legumes
Legumes such as black beans and red beans are rich in plant protein and dietary fiber, helping to maintain stable blood sugar levels and reduce fat production.
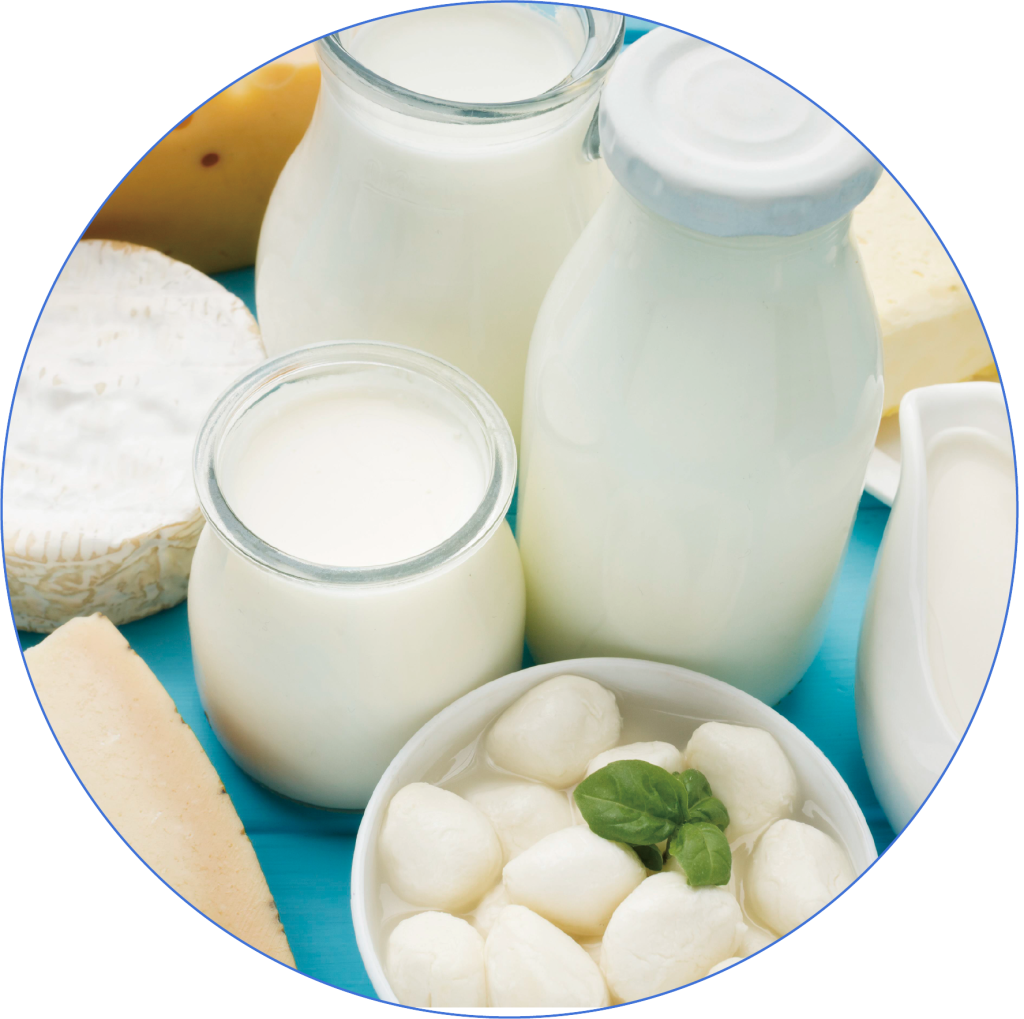

Low-fat Dairy Products
Low-fat milk and Greek yogurt are rich in protein and calcium, which help promote fat metabolism.
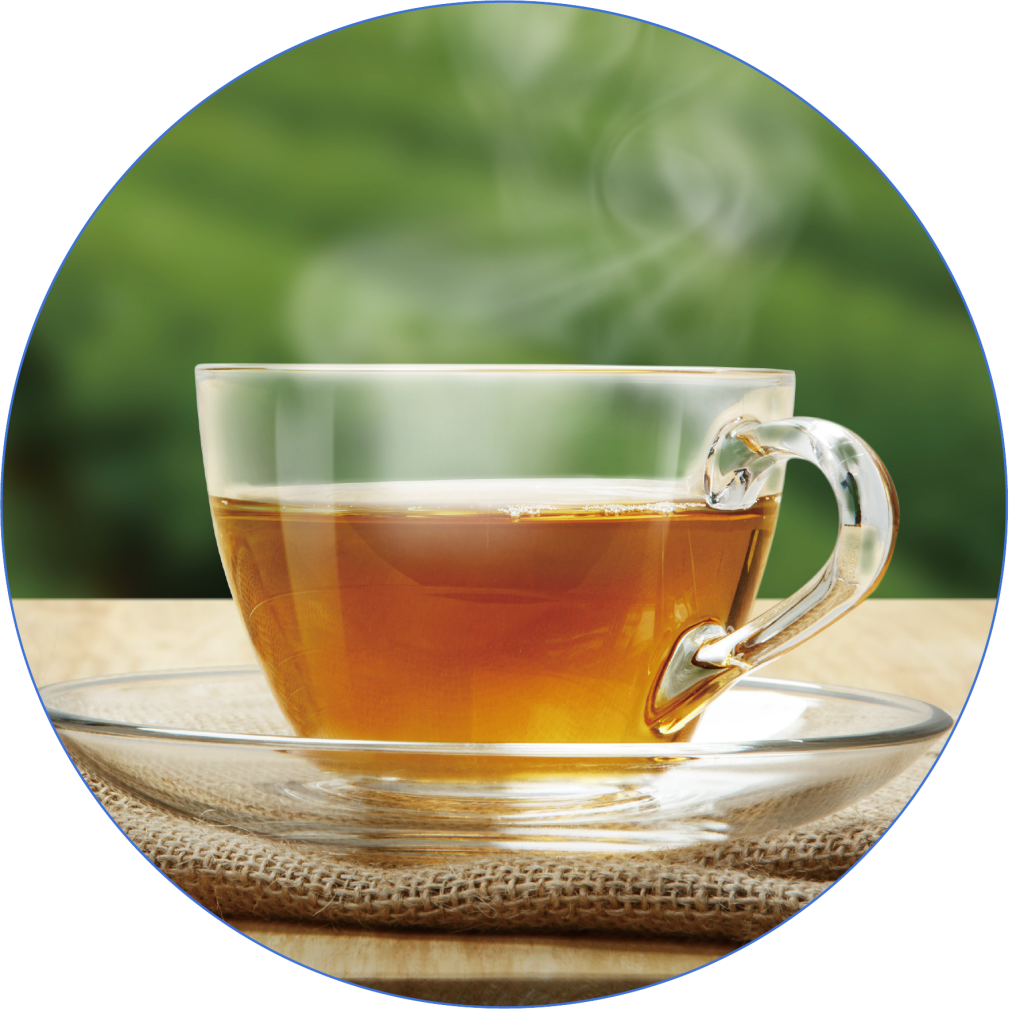

Green Tea
Green tea is rich in catechins, which promote fat burning and reduce visceral fat accumulation.
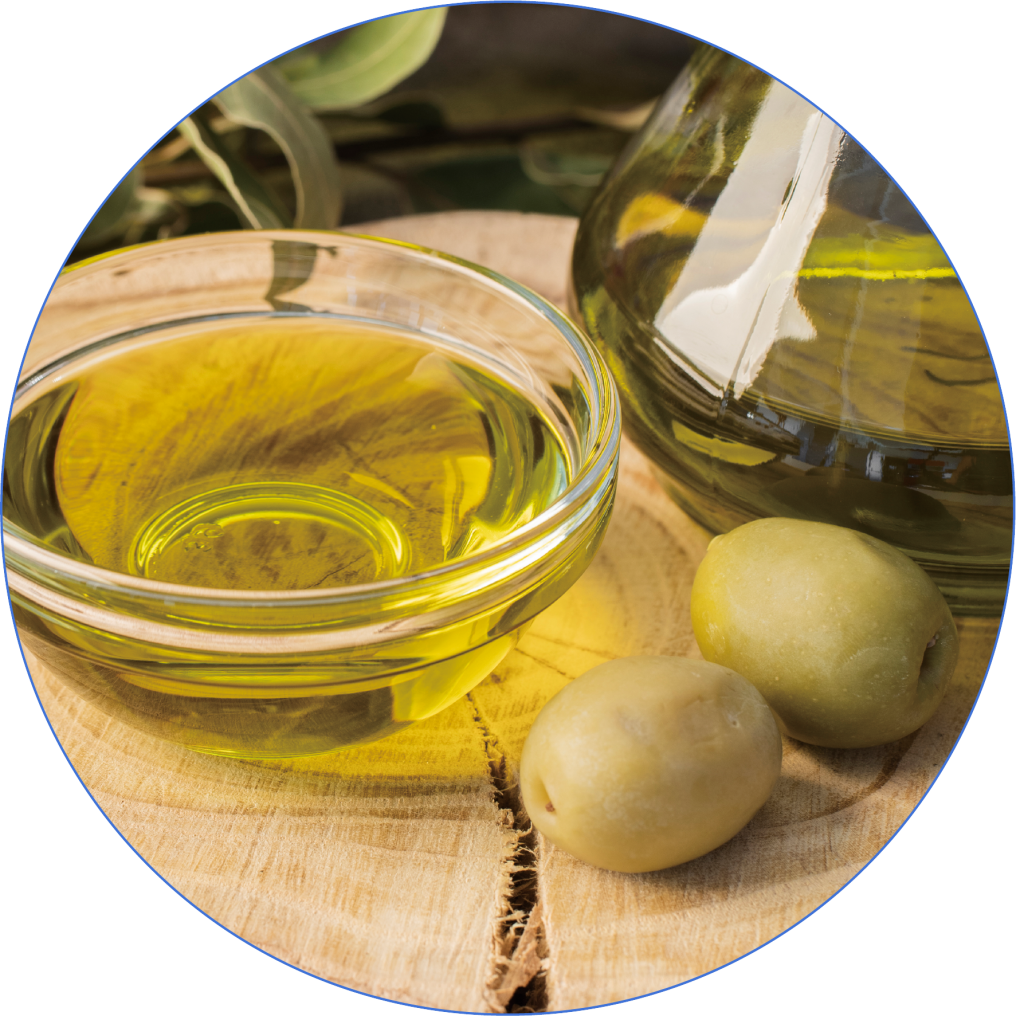

Olive Oil
Olive oil contains healthy monounsaturated fats that help reduce inflammation in the body and promote fat metabolism.
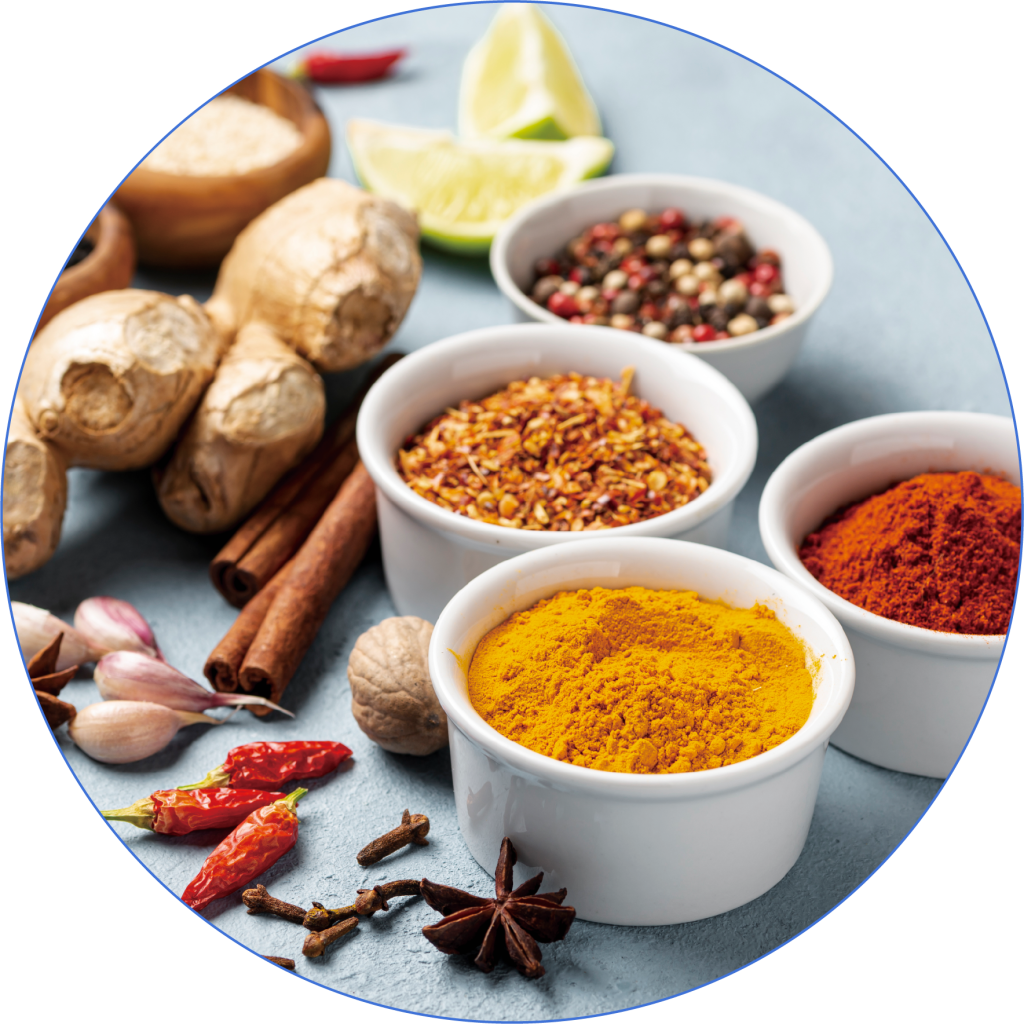

Spices
Spices such as turmeric and cinnamon have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that help boost metabolic rate and reduce fat accumulation.
—–Changing Your Habits for Better Health—–
The formation of visceral fat is often a result of absorbing more calories than are consumed. By adjusting your diet to include high-fiber vegetables, protein, and unsaturated fatty acids while reducing refined carbohydrates and high-sugar foods, you can effectively reduce up to 70% of visceral fat. Protect your health and embrace a vibrant life with Umi No Shizuku!
Back to the list